Fungus Infections
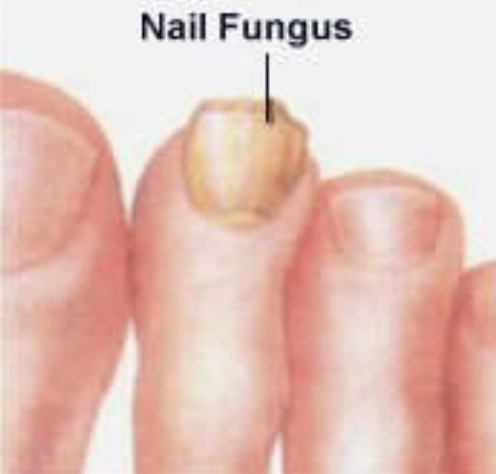
Fungal infection of the foot, or Tinea pedis (athletes foot), is a superficial infection caused by a dermatophyte. Dermatophytes are fungi that thrive in a nonviable tissue of the skin, nails, or hair. Trichophyton and Epidermophyton are the principle genera causing infection. Dermatophytosis can involve the entire plantar foot with extensive scaling, hyperkeratosis or even bulla formation. Infection between the toes (Tinea pedis interdigitalis) is quite common. When involvement of the nails occurs (onychomycosis) they take on a very thick, discolored (yellow/brown) appearance. Diagnosis is usually clinical, but a fungal culture or potassium hydroxide mount (KOH) of skin or nail scrapings can help diagnose unclear presentations by showing the presence of a fungal organism within the sample.
Tinea pedis can usually be resolved after several weeks of treatment with topical medications. Oral antifungals (i.e., Lamisil, diflucan,) can be used for extensive infection or poor topical response. Onychomycosis is more difficult to eradicate. Topical therapy results are poor, and recurrence is common after completion of successful oral treatment. Temporary nail avulsion or permanent nail removal (matrixectomy) may be indicated for several deformed, painful onychomycotic nails.